
- arrow_back Home
- keyboard_arrow_right 3D Printing
Introduction to SLS 3D Printing: Understanding Selective Laser Sintering

3D Printing Chris Wyatt 8 September 2024
Ever wondered about the magic that turns digital designs into tangible objects? In the realm of 3D printing, there are many fascinating processes, and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) stands out as a powerhouse. Let’s embark on a journey to understand the intricacies and marvels of SLS 3D printing and discover why it’s a game-changer in the world of manufacturing.
This image is property of xometry.asia.
Introduction to SLS 3D Printing: Understanding Selective Laser Sintering
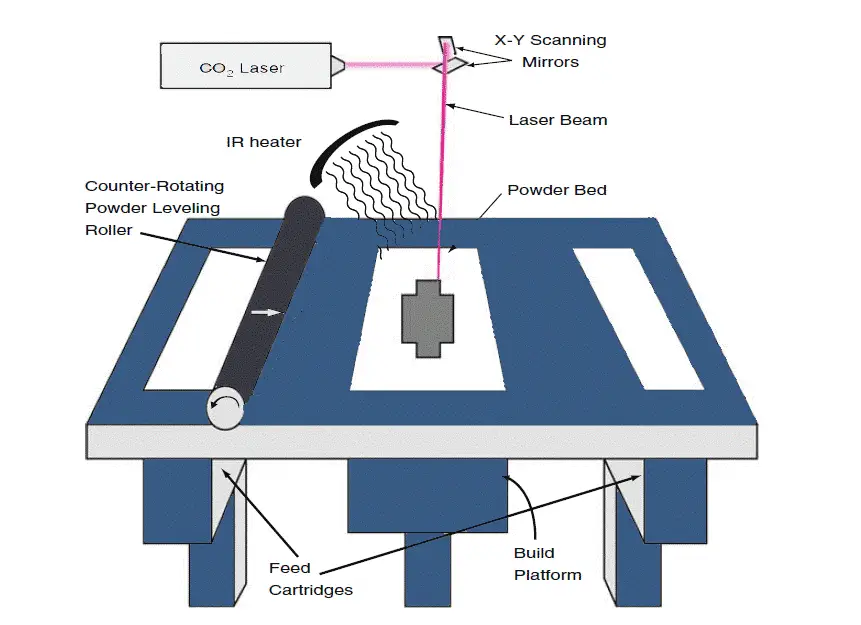
Selective Laser Sintering, or SLS, is an advanced form of additive manufacturing. This technology uses a high-power laser to fuse tiny particles of polymer powder into solid, three-dimensional structures. You might picture it as a method that gradually builds an object layer by layer, transforming a powdery substance into a durable, functional part.
Why SLS 3D Printing?
So, why should you care about SLS 3D printing? Well, it’s particularly revered for producing robust and functional components that stand the test of time. Whether it’s for rapid prototyping, small-batch production, or custom manufacturing, SLS brings your designs to life with precision and reliability.
Here’s a quick overview of what makes this technology intriguing:
- High-Power Laser: SLS employs a laser to sinter, or fuse, powder materials.
- 3D Models: The laser traces the design based on a digital 3D model.
- Versatile Applications: Ideal for both prototypes and end-use parts.
Process Overview of SLS 3D Printing
Understanding the process gives you insight into why SLS is so effective. Let’s break down how it works:
Layer by Layer: The Building Process
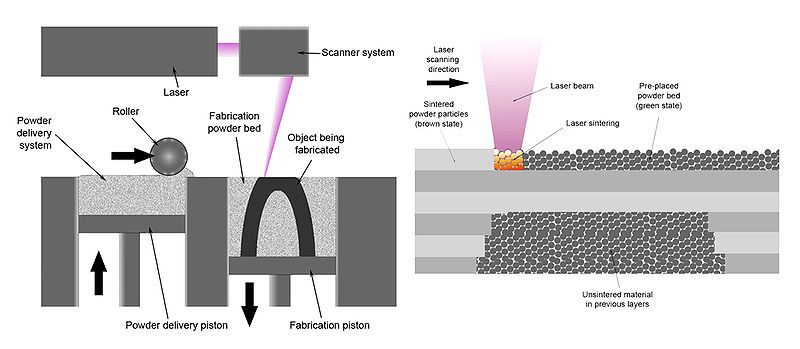
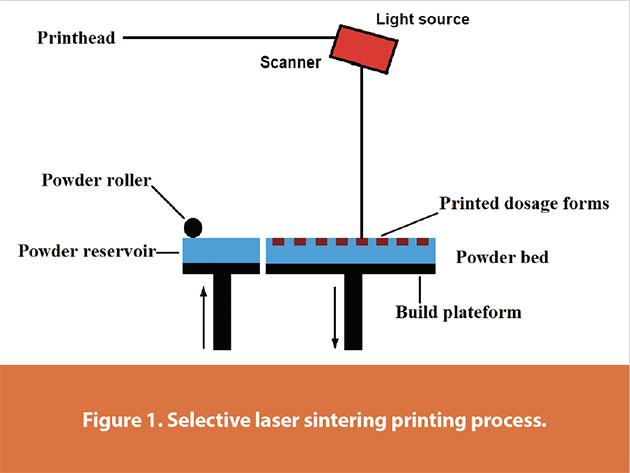
In an SLS 3D printer, polymer powder is spread across a build platform in thin, even layers. The laser precisely sinters the powder by following the cross-section of your 3D model. Here’s a step-by-step snapshot:
- Powder Dispersion: A thin layer of powder is spread in the build chamber.
- Laser Sintering: The laser traces and sinters the powder based on the model’s cross-section.
- Layer Lowering: The build platform lowers slightly to make room for the next layer.
- Repetition: This process repeats until the part is fully formed.
Post-Processing Essentials
Once your part is printed, it’s not quite ready to go. It requires cooling and several post-processing steps to achieve its final shape and properties. These include:
- Cooling: Parts must cool slowly to avoid thermal stress.
- Cleaning: Residual powder is removed from the surface. Common methods include air blasting or brushing.
- Media Blasting: For final touches, a media blaster can smooth out the part to give it a finished look.
Advantages of SLS 3D Printing
You’re probably curious about what makes SLS stand out among other 3D printing technologies. Let’s explore some of its key advantages:
Support-Free Printing
One big highlight of SLS printing is that it doesn’t require dedicated support structures. The unsintered powder surrounding the part provides all the support necessary, which is particularly useful for creating complex geometries without the hassle of additional material or manual removal of supports.
Complex Geometries
Speaking of complex geometries, SLS shines where other methods fall short. Its high degree of design freedom allows you to create intricate designs that might be impractical with traditional manufacturing methods.
Mechanical Properties
The parts created using SLS are known for their excellent mechanical properties. The strength and durability are comparable to those achieved with injection molding, making SLS an ideal choice for functional parts that need to perform under stress and strain.
Formlabs Fuse Series: Making SLS Accessible
You might think SLS 3D printing is only for large-scale industrial use. However, companies like Formlabs have revolutionized the accessibility of this technology.
Benchtop Industrial SLS Printers
Formlabs introduced the first benchtop SLS 3D printers, the Fuse Series, which are compact, user-friendly, and more affordable than traditional industrial machines.
Key Features
- High-Quality Parts: The Fuse printers produce parts with professional-quality finishes.
- Simplified Workflows: These machines are designed for ease of use, reducing the learning curve for new users.
- Compact Footprint: Their smaller size fits well in a variety of workspaces without needing extensive retrofitting.
The Fuse 1+ 30W Model
The Fuse 1+ 30W model takes it up a notch with a more powerful laser and improved powder handling capabilities, making it a more versatile and efficient option for diverse applications.
This image is property of formlabs-media.formlabs.com.
Materials Used in SLS 3D Printing
In discussing any 3D printing technology, you can’t overlook the importance of materials. The choice of material affects everything from the part’s durability to its flexibility.
The Reign of Nylon
Nylon is the reigning champion in SLS 3D printing, particularly Nylon 11 and Nylon 12. These materials are favored for their strength, durability, and overall functionality.
Nylon 11 and Nylon 12
- Nylon 11: Known for its toughness and flexibility, making it suitable for parts that need to absorb impact.
- Nylon 12: Offers a balance of strength and rigidity, ideal for creating robust mechanical components.
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is another material used in SLS, valued for its lightweight and functional properties. It’s especially handy for parts that need chemical resistance or lower weight.
Reinforced Materials
For specific applications, base materials can be reinforced with additives like glass or carbon fiber. This enhancement further boosts the mechanical properties of the part, making it even more suited for demanding applications.
Comparing SLS with Other 3D Printing Technologies
How does SLS stack up against other 3D printing technologies such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and Stereolithography (SLA)? Let’s compare:
Support Structures
- SLS: No support structures needed, thanks to the unfused powder acting as an in-built support.
- FDM: Requires additional material for support structures.
- SLA: Needs supports that can be intricate to remove without damaging the part.
Mechanical Properties
- SLS: Excellent mechanical properties, comparable to injection molding.
- FDM: Generally weaker, with visible layer lines and less isotropic strength.
- SLA: High resolution and surface finish but more brittle than SLS.
Cost and Build Volume
The cost and build volume can vary significantly based on the specific printer models and materials used. Here’s a snapshot:
| Technology | Initial Cost | Build Volume | Suitable for |
|---|---|---|---|
| SLS | High, but reduces with new models like the Fuse Series | Moderate to Large | Functional parts, complex geometries |
| FDM | Low | Small to Large | Prototypes, basic parts |
| SLA | Medium | Small to Moderate | High-detail, low-stress parts |

This image is property of i.ytimg.com.
Historical Context of SLS 3D Printing
Knowledge of a technology’s history enriches your understanding of its impact and evolution. The story of SLS 3D printing begins in the mid-1980s.
Pioneers of SLS
Dr. Carl Deckard and Dr. Joe Beaman developed the original concept of SLS at the University of Texas at Austin. Their pioneering work laid the foundation for what would become one of the most transformative manufacturing technologies.
Technological Evolution
From its inception, SLS has evolved tremendously, incorporating an ever-expanding range of materials and applications. Innovations in laser technology, material science, and software have continued to broaden the capabilities and accessibility of SLS 3D printing.
Modern-Day Innovations
Recent innovations, like those by Formlabs, have democratized SLS 3D printing. These advancements make it viable not just for large enterprises but for smaller businesses and even hobbyists looking to create high-quality parts in-house.
Cost and Accessibility of SLS 3D Printing
A common misconception is that SLS 3D printing is prohibitively expensive and exclusive to large companies. While this was somewhat true in the past, things are changing.
Traditional Costs
Historically, industrial SLS systems were costly and complex, often necessitating significant investment and specialized knowledge. This made them accessible primarily to large enterprises with ample resources.
The Fuse Series Solution
Formlabs’ Fuse Series embodies the modern shift towards accessibility. These systems are:
- Cost-Effective: Lower initial investment compared to traditional industrial machines.
- Simpler: User-friendly interfaces and straightforward workflows streamline the printing process.
- Compact: Their smaller footprint makes them suitable for a variety of workspaces without the need for significant infrastructure changes.
This image is property of cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net.
End-Use Production with SLS 3D Printing
Can SLS be used for end-use production, or is it limited to prototyping? Modern advances show that SLS is a formidable contender for producing final parts.
Affordable and Scalable
SLS 3D printing has become more affordable and scalable, making it a viable option for producing end-use parts. The agility of this technology allows for quick iterations, short lead times, and customization without the cost penalties typically associated with traditional manufacturing.
In-House Production vs. Outsourcing
Choosing between in-house production and outsourcing depends on various factors, including cost, control, and volume. Here’s a brief comparison:
| Criteria | In-House Production | Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Initial investment but lowers over time | Pay per part |
| Control | Full control over design and process | Limited control post-design |
| Lead Time | Shorter, immediate adjustments possible | Potential delays |
| Customization | High, instant modifications | Varied, can incur additional costs |
Resources for Further Learning
Interested in learning more? There are plenty of resources available to deepen your understanding of SLS technology and its applications.
Educational Materials
- White Papers: Detailed studies and technical papers provide in-depth knowledge.
- Webinars: Live and recorded sessions by experts offer insights and answer questions.
Sample Parts
Experiencing the quality of SLS 3D printing firsthand can be instructive. Many companies provide sample parts upon request, allowing you to touch and see the level of detail and robustness achievable with SLS.
Getting to grips with SLS 3D printing offers a glimpse into the future of manufacturing. From its intricate process to its broad range of applications, SLS stands poised to continue revolutionizing how we create and utilize 3D-printed parts. Whether you are a hobbyist or a professional, knowing the ins and outs of SLS opens up a world of new possibilities for your projects and innovations.
This image is property of media.americanpharmaceuticalreview.com.
About Ultimate 3D
Learn everything there is to know about 3D Printers and the different components and printing materials.
Site Links
Copyright 2024 Ultimate 3D





Be the first to leave a comment