- arrow_back Home
- keyboard_arrow_right Uncategorised
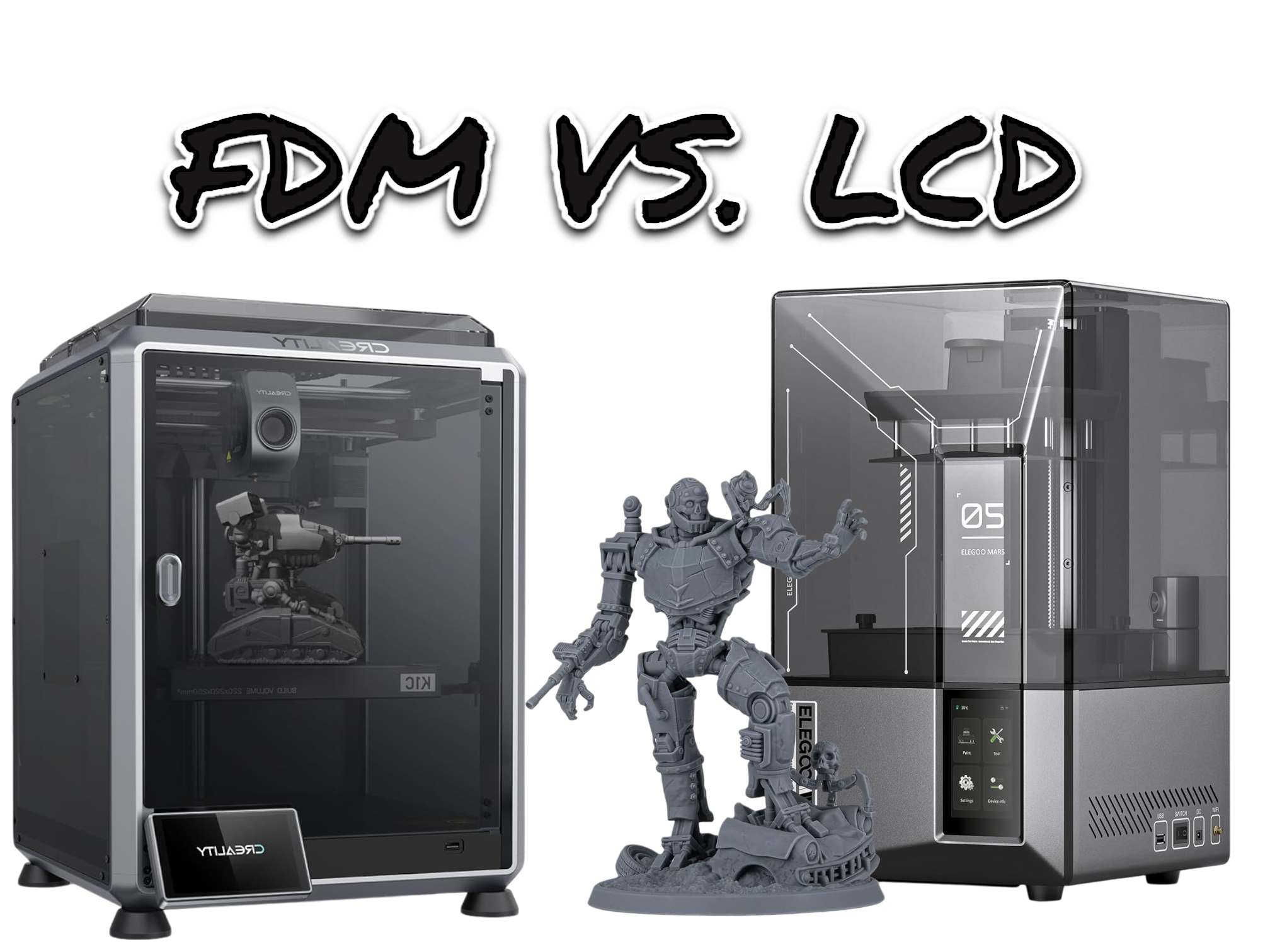
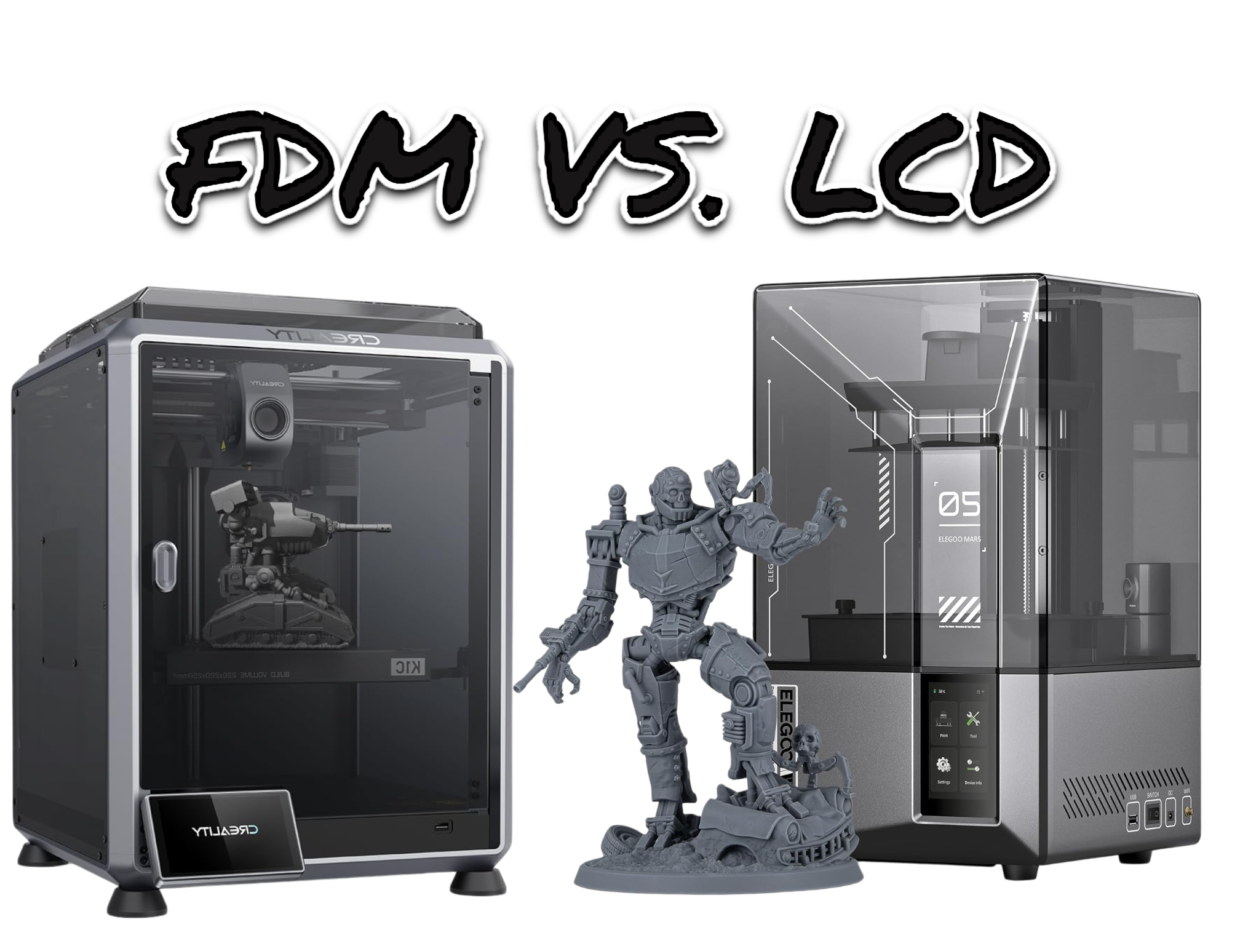
FDM vs. LCD Printers: What is the Best for Home Use?
Uncategorised Chris Wyatt 9 October 2024
Curious about which 3D printer is right for your home projects? Dive into our comparison of FDM and LCD printers to find out which one suits your needs best!

Understanding FMD
FMD, or Fused Deposition Modeling, is a widely used 3D printing method. It builds items layer by layer using melted plastic. This makes it perfect for creating detailed models and prototypes.
One of the best parts of FMD is its versatility. You can use a range of materials, from simple plastics to more complex blends. This flexibility helps hobbyists bring their creative ideas to life.
FDM printers are great for home use because they’re affordable and easy to operate. Even beginners can start printing 3D objects with minimal learning. This makes it a popular choice for those new to 3D printing.
Understanding LCD
LCD printers use UV light to harden resin and create detailed 3D models. This makes them great for complex designs and small parts that need precision.
These printers can produce smoother and more accurate models compared to other types. They are especially good for hobbyists who need high-quality results for their projects.
Because of their ability to make fine details, LCD printers are ideal for creating custom parts, miniatures, and intricate designs that would be difficult with other methods.
Print Quality
When it comes to print quality, LCD printers are generally known for their higher resolution compared to FDM printers. This difference makes LCD printers more suitable for detailed projects where precision is key.
FDM printers, while not offering the same high resolution as LCD printers, are favored for their versatility and ability to print larger objects. They are often chosen for projects where strength and durability are more important than fine details.
LCD printers use a screen to cure resin, resulting in smoother and more detailed finishes. This makes them ideal for printing small, intricate parts, such as miniatures and jewelry, where fine detail and surface smoothness are crucial.
Material Options
FDM printers are versatile, working with a range of thermoplastics like PLA and ABS. These materials are great for creating sturdy models and functional parts, making FDM an ideal choice for many home users.
LCD printers use liquid resin, which can produce highly detailed prints with smooth surfaces. This technology is perfect for hobbyists who need intricate models, such as miniatures or detailed prototypes.
When choosing between FDM and LCD for home use, consider what you’ll be printing. FDM offers durability and a variety of materials, while LCD provides superior detail and finish. Each has its strengths depending on your specific needs.
Ease of Use
Setting up an FDM printer is usually straightforward. You just need to follow a few steps, and most models come with detailed guides. This makes it a good pick for those who are new to 3D printing and want a hassle-free start.
When it comes to software, FDM printers often have user-friendly options. Many models are compatible with popular slicing software that offers a range of features without being too complex. This makes the printing process more approachable for hobbyists.
Maintenance for LCD printers can be a bit more involved than for FDM printers. You often have to deal with resin cleanup and ensure the screen remains clear. However, the higher detail in prints can be worth the extra effort for those seeking precision.
Print Speed
FDM printers often have slower print speeds compared to LCD printers because they build objects layer by layer using melted filament. This can be a drawback if you need to produce multiple models quickly, making LCD printers more suitable for time-sensitive projects.
LCD printers, on the other hand, use UV light to cure resin, allowing them to print entire layers at once. This makes them significantly faster than FDM printers, especially for detailed models. If speed is crucial, LCD printers are likely the better choice.
While FDM printers may be slower, they offer a broader range of materials and colors. This versatility can be beneficial for hobbyists interested in experimenting with different types of prints. Consider your priorities: speed with LCD printers or material variety with FDM printers.
Cost Efficiency
FDM printers usually have a lower upfront cost compared to LCD printers, making them a more affordable option for beginners. However, the cost of filament used in FDM printers can add up over time, especially for large or detailed prints.
LCD printers, while more expensive initially, often provide higher resolution prints. The cost of resin used in these printers can be higher than filament, but the quality of prints can justify the investment for those seeking detailed and intricate designs.
Maintenance and part replacement costs should also be considered. FDM printers might require more frequent part replacements like nozzles and belts. On the other hand, LCD printers may need occasional screen replacements, which can be more costly but less frequent.
Durability and Strength
When it comes to durability, FDM prints stand out. They are known to handle stress well, making them ideal for projects requiring strong and lasting parts. This quality makes FDM a great choice for home use where reliability is key.
FDM technology produces sturdy prints because it uses thermoplastic filaments that bond well. These prints can withstand various pressures and impacts, offering a dependable option for hobbyists who need durable models and parts for their projects.
On the other hand, LCD prints, while detailed, are often less durable. They are more suited for intricate designs that don’t need to endure much stress. Understanding these differences helps hobbyists choose the best method for their specific needs and projects.
Maintenance Needs
For a smooth printing experience, regular maintenance of FDM and LCD printers is essential. Clean the print bed and nozzles frequently to avoid clogs and ensure precise prints. A well-maintained printer saves time and reduces print failures.
FDM printers need their nozzles and extruders checked regularly. Make sure to clear any filament debris and check for wear and tear. This keeps the printer running smoothly and extends its lifespan, making it perfect for home use.
LCD printers require careful handling of the resin vat and screen. Clean the vat after every print and inspect the screen for any residue. Proper care ensures longer-lasting equipment and consistently high-quality prints, ideal for hobbyists.
Noise Levels
FDM printers often produce more noise due to their mechanical movements and fan cooling systems. This can be distracting in a quiet home environment, making it less ideal for those seeking a peaceful workspace.
LCD printers tend to be quieter than FDM printers. They use fewer moving parts and have a different printing process, which reduces noise significantly. This makes them a better choice for home use where noise levels are a concern.
When comparing FDM and LCD printers, it’s important to consider your home environment. If you need a quieter printer, an LCD model is generally the better option, providing a more pleasant experience without the constant background noise of an FDM printer.
Environmental Impact
FDM printers generally use PLA filament, which is biodegradable and derived from renewable resources like corn starch. This makes them a greener option compared to other materials, as they produce less environmental waste during printing.
LCD printers use resin, which is often toxic and not biodegradable. This means disposing of waste from LCD printing can be more harmful to the environment. Proper handling and disposal of resin are crucial to minimize its ecological impact.
When considering energy consumption, FDM printers typically use less power than LCD printers. This lower energy usage not only reduces electricity costs but also lessens the overall carbon footprint, making FDM a more eco-friendly choice for home use.
Customization Flexibility
FDM printers are great for those who enjoy tinkering and modifying their machines. You can easily swap out parts, upgrade components, and even build custom setups. This makes them perfect for hobbyists who love hands-on projects.
LCD printers, on the other hand, offer high precision and smooth finishes, ideal for creating detailed models and miniatures. While they are not as customizable as FDM printers, they excel in producing intricate designs that require minimal post-processing.
Both FDM and LCD printers offer a range of material options, each suited for different projects. FDM printers can use a variety of filaments like PLA, ABS, and PETG, while LCD printers work with various resins, allowing for more specialized applications.
Software Compatibility
Choosing the right software is key for a smooth 3D printing experience with FDM and LCD printers. Programs like Cura and PrusaSlicer are popular for FDM, offering user-friendly interfaces and a wide range of settings.
For LCD printers, software like ChiTuBox and Lychee Slicer are commonly used. These programs are designed to handle the detailed requirements of resin printing, providing features like automatic support generation and easy-to-use interfaces.
Many software options offer compatibility with both FDM and LCD printers, allowing hobbyists to switch between different types of projects seamlessly. This flexibility can enhance your 3D printing experience, making it more enjoyable and productive.
Safety Considerations
When using FDM printers at home, it’s important to ensure proper ventilation. FDM printers can release fumes from melted plastic, which might be harmful if inhaled in large amounts. Keeping your workspace well-ventilated helps mitigate this risk.
LCD printers use resin, which can be toxic if it comes into contact with skin. Always wear gloves and safety glasses when handling resin. Additionally, ensure your workspace is equipped with proper ventilation to avoid inhaling any harmful fumes.
Both FDM and LCD printers can get very hot during operation. Keep flammable materials away from your printer and never leave it unattended while it’s running. This reduces the risk of accidental fires and ensures a safe printing environment.
Best Use Cases
FDM printers are great for hobbyists who want to create strong and durable items. They are perfect for making functional parts, prototypes, and large models. These printers are known for their affordability and ease of use, making them a popular choice.
LCD printers excel in producing highly detailed and smooth objects. They are ideal for creating miniatures, jewelry, and intricate designs. With their ability to capture fine details, LCD printers are perfect for projects that require high precision and a polished finish.
For home use, FDM printers are often preferred for their cost-effectiveness and versatility, while LCD printers are chosen for their superior detail and finish quality. Depending on the project, hobbyists can select the type that best fits their needs, balancing cost and detail.
Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing between FDM and LCD printers for home use depends on your specific needs. FDM printers are great for larger, functional prints and are generally easier to use. On the other hand, LCD printers offer higher detail and are perfect for intricate designs. Consider what you value most in your 3D printing projects to make the best choice. Happy printing!
Questions & Answers:
Question: What is FMD and how does it work?
Answer: FMD, or Fused Deposition Modeling, is a 3D printing method that builds items layer by layer using melted plastic. It is widely used for creating detailed models and prototypes.
Question: What are the advantages of using FDM printers for home use?
Answer: FDM printers are affordable, easy to operate, and versatile. They can use a range of materials and are suitable for beginners, making them a popular choice for home use.
Question: How do LCD printers create 3D models?
Answer: LCD printers use UV light to harden resin, creating detailed 3D models. This technology is great for complex designs and small parts that need precision.
Question: Which type of printer offers better print quality, FDM or LCD?
Answer: LCD printers generally offer higher resolution and smoother finishes compared to FDM printers, making them more suitable for detailed projects where precision is key.
Question: What types of materials can FDM printers use?
Answer: FDM printers can work with a range of thermoplastics like PLA and ABS, which are great for creating sturdy models and functional parts.
Question: Are LCD printers more difficult to maintain than FDM printers?
Answer: Yes, LCD printers often require more involved maintenance, such as resin cleanup and screen care, compared to FDM printers which mainly need nozzle and extruder checks.
Question: Which type of printer is faster, FDM or LCD?
Answer: LCD printers are generally faster because they use UV light to cure resin in entire layers at once, whereas FDM printers build objects layer by layer using melted filament.
Question: Are FDM printers more cost-efficient than LCD printers?
Answer: FDM printers usually have a lower upfront cost and can use a variety of filaments. However, the cost of filament can add up over time. LCD printers have a higher initial cost but provide higher resolution prints.
Question: Which type of printer produces more durable prints?
Answer: FDM printers produce more durable prints because they use thermoplastic filaments that bond well, making them ideal for projects requiring strong and lasting parts.
Question: What safety considerations should be taken when using FDM and LCD printers?
Answer: For FDM printers, ensure proper ventilation to avoid inhaling fumes from melted plastic. For LCD printers, wear gloves and safety glasses when handling resin and ensure proper ventilation to avoid inhaling harmful fumes.
About Ultimate 3D
Learn everything there is to know about 3D Printers and the different components and printing materials.
Site Links
Copyright 2024 Ultimate 3D





Be the first to leave a comment