- arrow_back Home
- keyboard_arrow_right 3D Printing
Exploring Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and Its Filament Types for 3D Printing

3D Printing Chris Wyatt 3 June 2024
In the fascinating world of 3D printing, Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) stands out as one of the most widely used techniques. With its array of filament types like PLA, ABS, and PETG, FDM printing offers diverse possibilities for various applications. This friendly guide explores FDM, discussing its distinct filament types and highlighting essential safety considerations to ensure a smooth and safe printing experience. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional, understanding the nuances of FDM and its materials will elevate your 3D printing projects to new heights. Have you ever found yourself marveling at the intricate creations of a 3D printer and wondered about the mechanics behind it all? Well, you’re in for an exciting dive into the world of Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and the various types of filaments that power these amazing machines!

Understanding Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
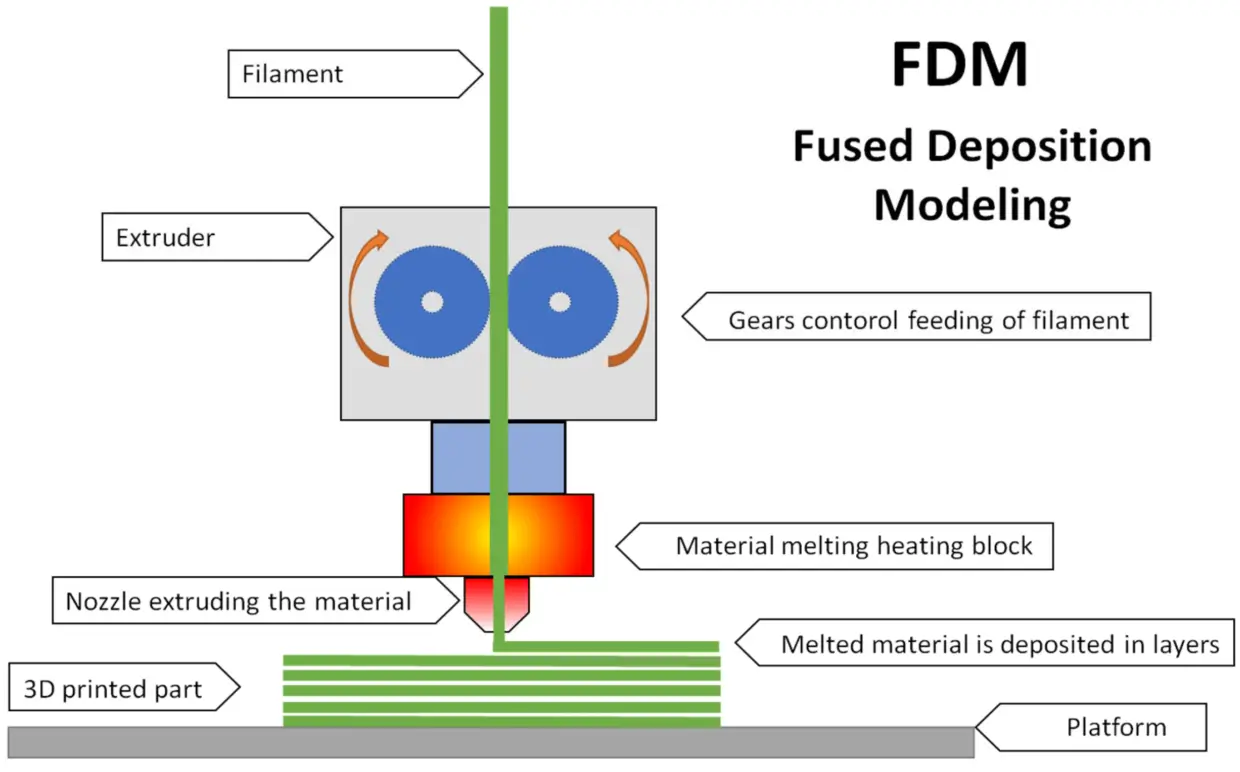
Fused Deposition Modeling, or FDM, is a popular 3D printing technology that you might have come across. It’s like the superstar of the 3D printing world due to its accessibility and simplicity. In essence, FDM works by extruding small beads of thermoplastic material, which are then layered to form an object. Imagine a hot glue gun controlled by a computer that layers glue meticulously to build shapes and structures—pretty fascinating, right?
How FDM Works
The FDM process starts with feeding a spool of thermoplastic filament into a heated printer extruder. This extruder melts the filament and then precisely deposits it onto the build platform layer by layer, following a digital blueprint. The material cools down and hardens immediately, creating a solid structure. The build platform moves down incrementally after each layer is deposited, allowing the object to grow vertically.
Advantages of FDM
So why is FDM so widely loved? Here are a few reasons:
- Affordability: FDM printers are generally more affordable compared to other 3D printing technologies.
- Accessibility: Easy to use, making them perfect for beginners and hobbyists.
- Variety of Materials: A wide range of filament types to choose from, helping you create diverse projects.
Safety Concerns
While FDM is exciting, it does come with its share of safety considerations. For one, the heated extruder and build platform can get very hot—carelessness can lead to burns. Additionally, melting thermoplastics can emit fumes, which may be harmful if inhaled over long periods. Always ensure your 3D printing area is well-ventilated, and don’t forget to handle the equipment carefully.
Types of Filaments Used in FDM
One of the most exciting aspects of FDM printing is the variety of materials you can use. Each filament type has distinctive properties, making some better suited for specific applications than others. Let’s explore the most common filament types you’ll encounter.
PLA (Polylactic Acid)
PLA is perhaps the most commonly used filament in FDM printing. Made from renewable resources like cornstarch or sugarcane, it’s a favorite due to its eco-friendliness and ease of use.
Pros:
- Easy to print with
- Biodegradable
- Minimal warping
Cons:
- Not heat-resistant
- Brittle compared to other filaments
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
ABS is another popular filament known for its strength and durability. It’s often used to create sturdy items like LEGO blocks and automotive parts.
Pros:
- Strong and durable
- More flexible than PLA
- Heat-resistant
Cons:
- Emits fumes
- Prone to warping
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-Modified)
PETG combines some of the best properties of PLA and ABS, offering good strength and flexibility without the intense fumes.
Pros:
- Strong and durable
- Less brittle than PLA
- Resistant to chemicals
Cons:
- Can be stringy while printing
- Requires fine-tuning to get the settings right
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane)
If you’re looking for flexibility, TPU might just be your go-to material. It’s rubber-like, making it perfect for objects that need to withstand wear and tear.
Pros:
- Highly flexible
- Impact-resistant
- Durable
Cons:
- Can be challenging to print with
- Requires a slower print speed
Nylon
Nylon is strong, flexible, and comes with a touch of engineering excellence. It’s commonly used in tools, functional prototypes, and even gears.
Pros:
- Strong and durable
- Flexible
- High abrasion resistance
Cons:
- Sensitive to moisture
- Requires high printing temperature
Specialty Filaments
There are many other specialty filaments you can venture into, such as wood-filled, metal-filled, and glow-in-the-dark filaments. Each type brings unique attributes, allowing for highly customized prints.
Here’s a quick reference table to help you compare these popular filaments:
| Filament Type | Main Advantages | Main Disadvantages | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | Eco-friendly, easy to use | Not heat-resistant, brittle | Prototypes, models |
| ABS | Strong, durable, heat-resistant | Emits fumes, warps easily | Automotive parts, toys |
| PETG | Durable, chemical-resistant | Stringy, requires fine-tuning | Bottles, containers |
| TPU | Highly flexible, impact-resistant | Hard to print, slow speed | Wearables, phone cases |
| Nylon | Strong, flexible, abrasion-resistant | Moisture-sensitive, high temp | Tools, gears |
Selecting the Right Filament for Your Project
Choosing the right filament can be overwhelming given the options. Your choice should depend on the specific requirements of your project.
Consider the Application
The first thing to think about is what you’re making. Is it a prototype, a functional part, or a decorative item? For instance, if you’re printing a prototype, PLA is generally sufficient. But if you need something durable, consider ABS or PETG.
Printer Compatibility
Ensure your printer supports the filament you intend to use. For example, not all 3D printers are equipped to handle flexible materials like TPU or high-temperature filaments like Nylon.
Environmental Factors
Different filaments have varying requirements for temperature and humidity. For instance, Nylon absorbs moisture from the air, which can affect the quality of your print. Ensuring proper storage conditions can go a long way in maintaining print quality.
Ease of Use
If you’re just starting, it’s advisable to begin with something easy like PLA. As you gain more experience, you can experiment with more complex or challenging filaments.
Tips for Optimizing Your FDM Printing Experience
A successful 3D print is often the sum of several factors coming together perfectly. Here are some tips to help you make the most out of your FDM printing journey.
Fine-Tuning Printer Settings
Every filament type has its own optimal settings in terms of temperature, speed, and cooling. Investing time to fine-tune these settings for each filament can dramatically improve the quality of your prints.
Bed Adhesion
Poor bed adhesion can ruin your print. Materials like ABS are notorious for this issue. Using a heated bed and applying adhesives like glue sticks or painter’s tape can aid in better adhesion.
Performing Maintenance
Regularly maintain your printer by cleaning the nozzle and checking for any mechanical issues. This ensures that your printer runs smoothly and produces high-quality prints consistently.
Storing Filaments Properly
Filaments can degrade over time due to exposure to air and moisture. Store them in airtight containers with desiccants to extend their lifespan and maintain print quality.
Ventilation
Good ventilation is crucial, especially when using filaments like ABS that emit fumes. Ensure your 3D printing area is well-ventilated to maintain a healthy environment.

Challenges and Troubleshooting in FDM Printing
FDM printing isn’t without its challenges. Here are some common issues you might encounter and how to troubleshoot them.
Warping
Warping occurs when your print detaches from the build platform, leading to skewed or incomplete prints.
Solution:
- Use a heated bed and ensure it’s set to the right temperature for your filament.
- Apply adhesives like a glue stick or painter’s tape to the build platform.
Stringing
Stringing happens when thin, hair-like threads appear between different sections of your print.
Solution:
- Adjust retraction settings to ensure the filament is pulled back slightly when the print head travels.
- Increase the print speed to minimize the time the extruder spends in one place.
Layer Shifting
Layer shifting occurs when one or more layers in your print shift from their intended position.
Solution:
- Check for any loose belts or gears.
- Ensure the build platform is level and stable.
Under-Extrusion
Under-extrusion happens when less material is extruded than needed, leading to gaps or weak spots in your print.
Solution:
- Increase the print temperature to ensure the filament flows smoothly.
- Check for any clogs or blockages in the nozzle.
The Future of FDM Printing
The world of FDM printing is continuously evolving, with innovations and advancements happening at a rapid pace.
New Materials
New and advanced filaments are constantly being developed. These materials offer unique properties like enhanced flexibility, greater strength, and specialized uses, expanding the horizons of what’s possible with FDM printing.
Improved Printers
FDM printers are becoming more sophisticated and user-friendly. Features like auto bed leveling, improved nozzle designs, and higher resolution are making it easier to achieve professional-grade prints at home.
Sustainability
With growing awareness about sustainability, there’s a push towards developing more eco-friendly filaments and recycling programs. This ensures that 3D printing can be an environmentally responsible option.
Applications in Various Industries
FDM printing is making significant inroads in fields like healthcare, automotive, and aerospace, among others. From creating patient-specific prosthetics to producing lightweight parts for spacecraft, the applications are vast and varied.
Conclusion
Exploring FDM printing opens up a world of creativity and innovation. Whether you’re a hobbyist making small trinkets or an engineer prototyping new designs, the possibilities are endless. Understanding the different filament types and how to optimize your printing process will go a long way in ensuring successful and high-quality prints. So go ahead, dive into this fascinating world and start creating!
Your journey into Fused Deposition Modeling and the various filament types hopefully feels a bit clearer and more approachable. Have fun experimenting and pushing the boundaries of what you can create with your 3D printer!
About Ultimate 3D
Learn everything there is to know about 3D Printers and the different components and printing materials.
Site Links
Copyright 2024 Ultimate 3D








Be the first to leave a comment