
- arrow_back Home
- keyboard_arrow_right 3D Printing
Direct Drive Vs Bowden Feed

3D Printing Chris Wyatt 2 July 2024
In the realm of 3D printing, understanding the disparities between direct drive and Bowden feed systems is paramount for optimizing machine performance and achieving desired print quality. Direct drive systems position the extruder motor in close proximity to the print head, ensuring efficient filament extrusion and superior control over retractions and print details. Conversely, Bowden feed systems utilize a longer tube to distance the extruder motor from the print head, effectively reducing the overall weight of the print head and enabling faster print speeds. However, this configuration can lead to challenges in precise filament control and increased retraction complexity. When determining machine compatibility, you must consider the specific requirements of your printing projects, including the intricacies of the filament types used and the desired balance between print speed and accuracy. Have you ever wondered about the differences between direct drive and Bowden feed systems in 3D printing? As you delve deeper into the world of 3D printing, the phrase “direct drive vs Bowden feed” may have crossed your path multiple times. This article aims to elucidate the distinctions between these two filament feeder mechanisms, their compatibility with various machines, and help you decide which system might suit your needs best.

Introduction to 3D Printing Filament Feed Systems
Understanding the mechanism that feeds the filament into the extruder is crucial for optimizing your 3D printing setup. The two primary systems employed in modern FDM/FFF 3D printers for filament feeding involve either a direct drive or a Bowden setup. These mechanisms offer differing advantages and challenges depending on the type of 3D printing tasks you aim to undertake.
The Basics: What is a Filament Feeder?
A filament feeder is a mechanism designed to drive the filament into the extruder of your 3D printer. It ensures that the material is accurately supplied to the hot end where it is melted and then deposited layer by layer to create your print. The two predominant types of filament feeders are the direct drive and Bowden feed systems, each offering distinct operational capabilities.
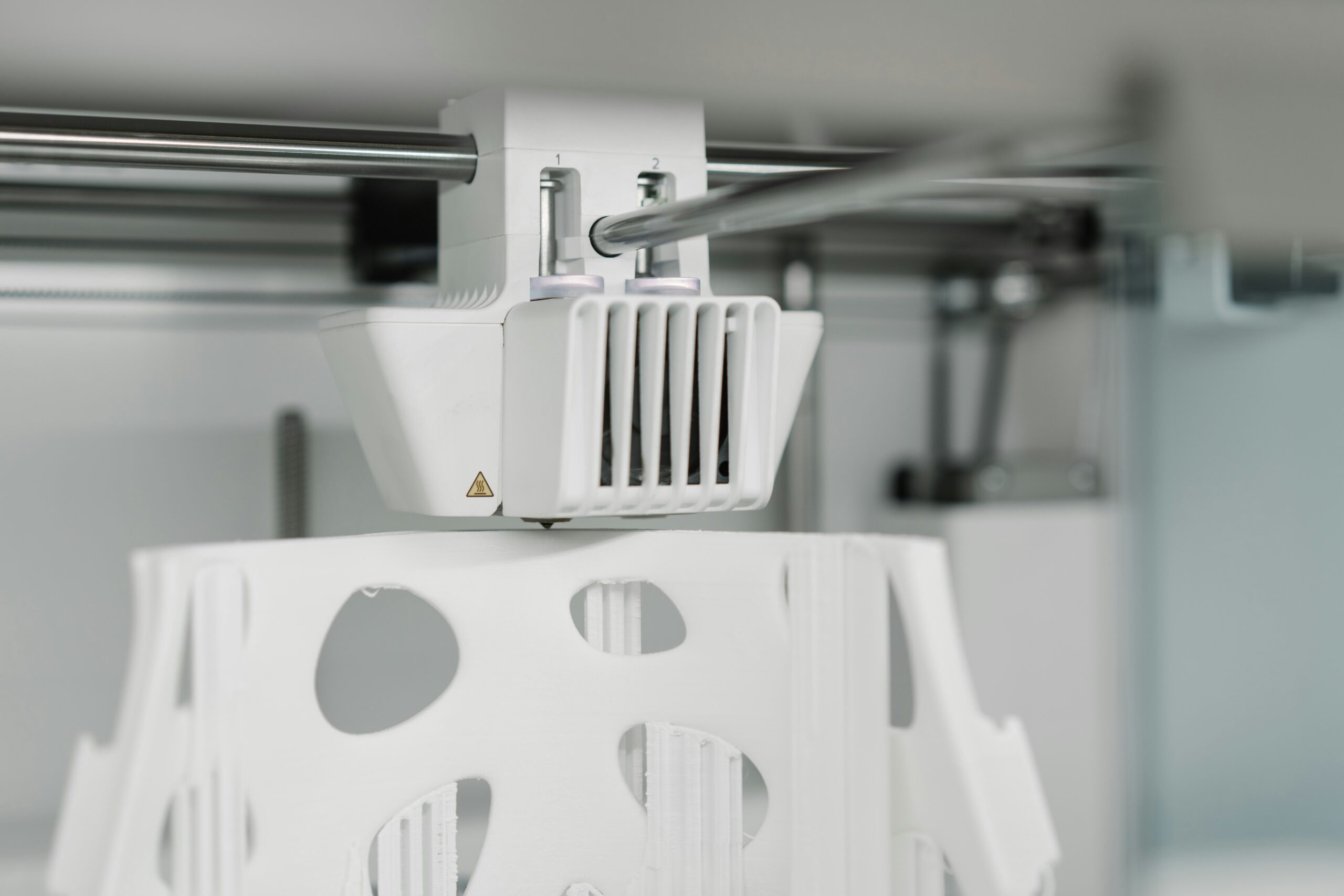
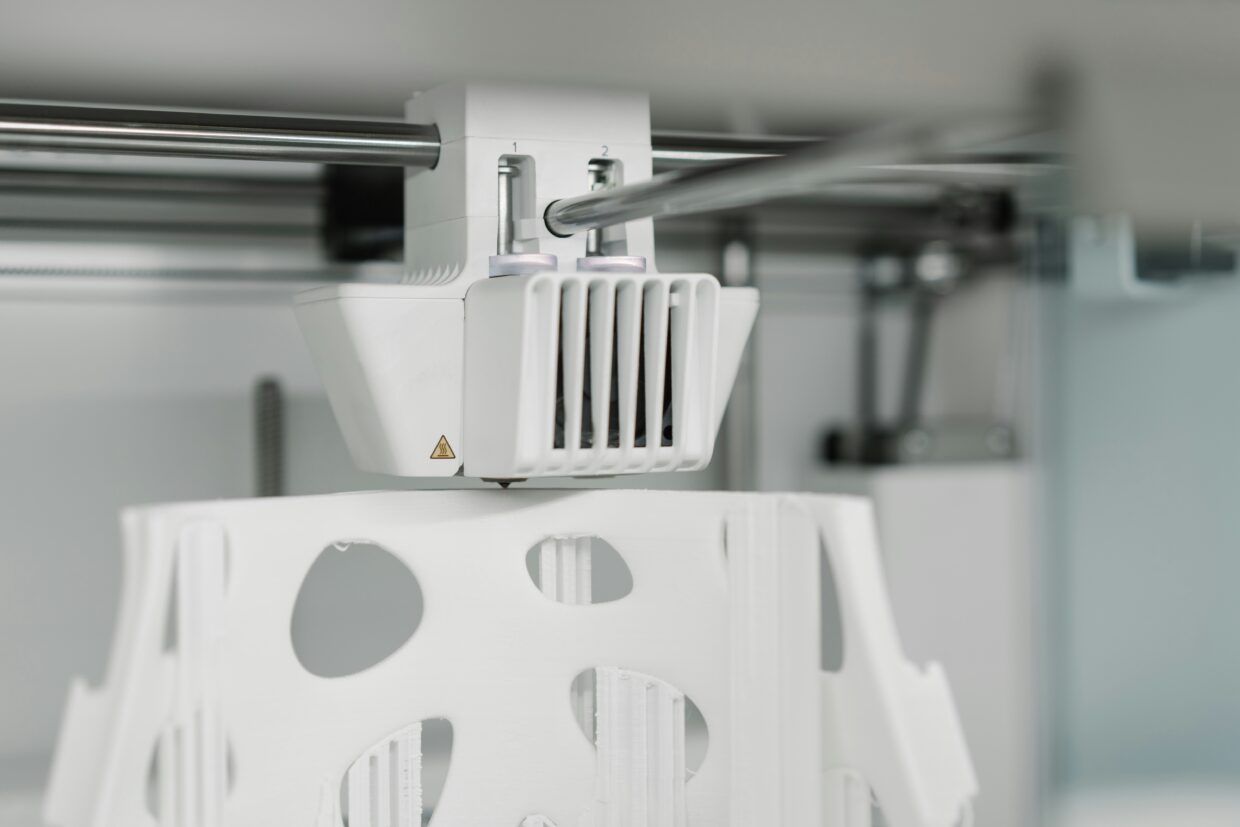
Direct Drive System
What is Direct Drive?
In a direct drive system, the filament drive mechanism is mounted directly on the extruder. This design allows for a more straightforward filament path, significantly reducing the distance between the drive gear and the hot end nozzle.
Advantages of Direct Drive Systems
Better Handling of Flexible Filaments
One of the most substantial benefits of a direct drive system is its superior ability to handle flexible filaments like TPU. The shorter filament path reduces the chances of filament buckling or tangling, thus ensuring more reliable extrusion of flexible materials.
Improved Retraction Control
Direct drive systems offer finer control over filament retraction, minimizing issues like stringing and oozing. The immediate response from the drive motor to the hot end means that extruder retraction can be more precisely adjusted.
Disadvantages of Direct Drive Systems
Added Weight on the Print Head
The most notable drawback of a direct drive system is the additional weight it places on the print head. This added weight can reduce the printer’s maximum speed and the overall agility of the printer, sometimes resulting in decreased print quality at higher speeds due to increased inertia.
Potential for Motor Overheating
Because the motor responsible for filament feeding is located on the print head, it is more susceptible to overheating, which could lead to printing failures and decreased motor life expectancy.

Bowden Feed System
What is Bowden Feed?
In a Bowden feed system, the drive mechanism is mounted away from the extruder, typically on the printer’s frame. The filament is pushed through a PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) tube that guides it to the hot end.
Advantages of Bowden Feed Systems
Reduced Weight on the Print Head
The primary advantage of a Bowden feed system is that it significantly reduces the weight on the print head. This reduction in weight allows for faster print speeds and improved agility, which can result in better print quality at higher speeds.
Increased Print Speed
Since the print head weighs less, the printer can move more quickly, enhancing the overall printing efficiency. This setup is particularly useful for larger prints where speed is a critical factor.
Disadvantages of Bowden Feed Systems
Challenges with Flexible Filaments
One of the main drawbacks of the Bowden feed system is its difficulty in handling flexible filaments. The longer filament path through the Bowden tube increases the likelihood of filament buckling and kinking, which can result in print failures.
Complicated Retraction Settings
Since the filament path in a Bowden setup is longer, achieving optimal retraction settings can be more challenging. Incorrect retraction settings may lead to problems like stringing and oozing, which can compromise print quality.

Comparison: Direct Drive Vs Bowden Feed
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each system can help you make an informed decision about which setup is better suited to your needs. Here’s a comparison table summarizing key points:
| Criteria | Direct Drive | Bowden Feed |
|---|---|---|
| Handling Flexible Filaments | Excellent | Challenging |
| Print Head Weight | High | Low |
| Retraction Control | Precise | Complex |
| Print Speed | Moderate | Fast |
| Motor Overheating | Possible | Less Likely |
| Filament Path | Short | Long |
| Suitable Applications | Prototyping, Flexible Materials | Large Prints, High-Speed Requirements |
Machine Compatibility
When considering upgrading or choosing a 3D printer, it’s crucial to evaluate the compatibility of these feeder systems with various machine types.
Direct Drive Compatibility
Most 3D printers can be adapted to a direct drive system. However, this setup is particularly suitable for machines designed for detailed, small, or intricate prints requiring high precision and control, especially when flexible materials are involved.
Bowden Feed Compatibility
Bowden feed systems are commonly found in delta and Cartesian printers where print speed and reduced moving mass are prioritized. This setup is ideal for large-scale prints and tasks where the use of rigid filaments is predominant.
Practical Considerations
When selecting between direct drive and Bowden systems, consider the following factors:
- Print Material: If you frequently use flexible filaments like TPU, a direct drive system is generally more reliable.
- Print Size and Complexity: For large prints that require quick deposition rates, a Bowden setup can enhance efficiency.
- Machine Specifications: Verify whether your 3D printer can accommodate the additional weight of a direct drive system or if it’s better suited to the lighter Bowden feed mechanism.
Optimization Tips for Each System
Once you have decided on a filament feed system, maximizing its performance is essential for achieving optimal print quality.
Optimizing Direct Drive
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure that the drive gears are clean and free from debris to maintain consistent filament feeding.
- Cooling Management: Use effective cooling systems to prevent motor overheating, which can compromise printing efficiency.
- Tuning Retraction Settings: Fine-tune retraction settings in your slicer software to minimize stringing and oozing.
Optimizing Bowden Feed
- Tube Quality: Utilize high-quality, low-friction Bowden tubes to facilitate smoother filament movement.
- Retraction Calibration: Spend time calibrating retraction settings to account for the longer filament path, which is crucial for reducing print artifacts.
- Sturdy Mounting: Ensure that the Bowden tube is securely mounted to prevent any unnecessary movement that could affect filament feeding accuracy.
Conclusion
Selecting between a direct drive and a Bowden feed system is not a one-size-fits-all decision. It hinges on your specific printing needs, materials, and machine capabilities. Direct drive systems excel in handling flexible filaments and offering precise retraction control but come with the trade-off of added weight and potential motor overheating. Bowden feed systems, on the other hand, provide reduced weight on the print head and increased print speeds, though they may pose challenges in handling flexible filaments and require more meticulous retraction calibration.
Understanding these distinctions and practical considerations will enable you to make a more informed and effective choice for your 3D printing endeavors. Whether you prioritize material versatility or speed, recognizing the capabilities and limitations of each system will allow you to optimize your 3D printing process to achieve the best possible results.
About Ultimate 3D
Learn everything there is to know about 3D Printers and the different components and printing materials.
Site Links
Copyright 2024 Ultimate 3D








Be the first to leave a comment