- arrow_back Home
- keyboard_arrow_right Technology
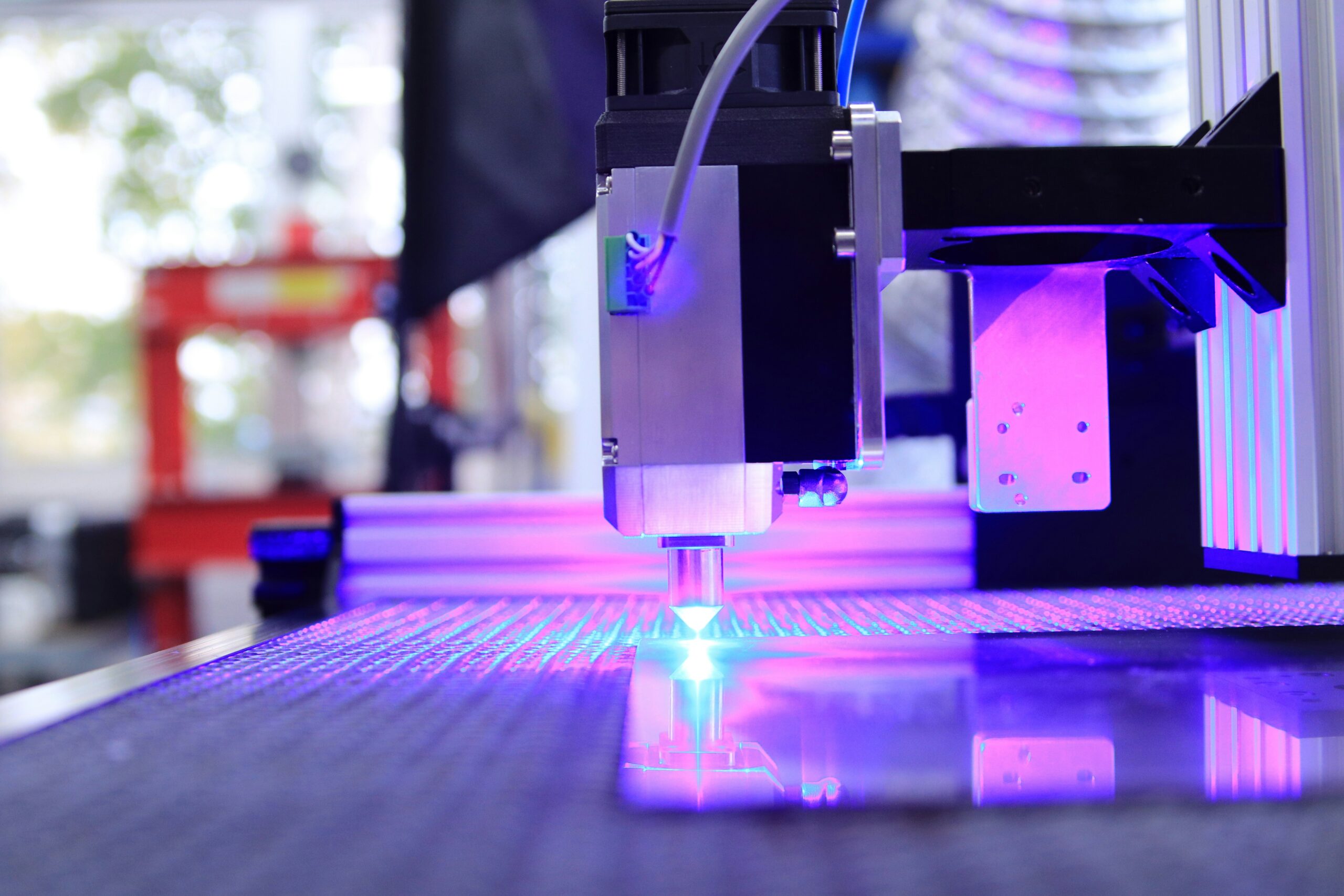
The Industrial Applications of 3D Printing
Technology Chris Wyatt 10 June 2024
In “The Industrial Applications of 3D Printing in Cost Reduction,” you will explore how advanced 3D printing technology revolutionizes industries by significantly lowering production costs. This article delves into the multifaceted benefits of 3D printing, highlighting its capacity to produce prototypes and products more cost-effectively, streamline the creation of useful tools, and facilitate the design of custom works tailored to specific industry needs. Through precise examples and detailed analysis, you will gain a comprehensive understanding of how 3D printing not only optimizes manufacturing processes but also impacts economic efficiency across various sectors. Have you ever considered how the integration of advanced technologies can significantly reduce production costs in various industries? One of the groundbreaking solutions gaining traction today is 3D printing. By harnessing the power of additive manufacturing, businesses are seeing substantial cost reductions across multiple sectors.
The Industrial Applications of 3D Printing in Cost Reduction
Introduction to 3D Printing and Its Relevance in Industry
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, refers to the process of creating a three-dimensional object from a digital model by adding material layer by layer. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, which often involve subtractive processes like cutting or drilling, 3D printing adds material only where needed, minimizing waste and optimizing resource use. This technology is revolutionizing various industries by offering significant cost-saving benefits.
Economic Benefits of 3D Printing
Prototyping and Product Development
One of the primary advantages of 3D printing is its ability to streamline the prototyping and product development process. Traditional prototyping methods can be costly and time-consuming, requiring the development of molds or the manual crafting of prototypes.
| Advantages | Traditional Prototyping | 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | High | Low |
| Time | Weeks to Months | Hours to Days |
| Design Flexibility | Low | High |
| Material Use | Wasteful | Efficient |
By shifting to 3D printing, you can reduce both the time and cost associated with prototype production, allowing for quicker iterations and faster development cycles.
Tooling and Custom Tools
3D printing also allows for the creation of custom tools and fixtures, eliminating the need to invest in expensive and time-consuming conventional tooling processes. With 3D printing, you can design and produce customized tools that are tailored to specific tasks, improving precision and effectiveness in manufacturing operations.
Another considerable advantage lies in the adjustability of designs. If a tool needs modifying, it can be easily tweaked and reprinted, making the entire process of tool creation not only cost-effective but also highly flexible.
Reducing Manufacturing Costs
Material Efficiency
When it comes to material use, 3D printing excels in minimizing waste. Traditional manufacturing often involves material removal from a larger block, leading to substantial waste. Additive manufacturing employs precise material placement, ensuring that you only use what is necessary for the build.
For instance, industries such as aerospace and automotive, where lightweight materials are essential, benefit enormously from these efficiencies. The saved material costs add up, providing a significant reduction in overall manufacturing expenses.
Labor Costs
Another area where 3D printing impacts cost is in labor. Traditional manufacturing processes frequently involve multiple steps, each requiring specialized skills and labor. By contrast, 3D printing often consolidates these steps into a single process, reducing the need for multiple operators and specialized labor.
Moreover, the automation involved in 3D printing means fewer human errors, leading to higher-quality products and lower costs associated with defect management and rework.
Customization and Small Batch Production
3D printing excellently caters to customization and small batch production without the high costs associated with traditional manufacturing. This is particularly useful for industries needing bespoke items or limited production runs.
Personalized Products
Industries such as healthcare greatly benefit from the customization offered by 3D printing. For example, custom prosthetics and dental implants can be produced at a fraction of the cost and time compared to traditional methods. This personalized approach enhances patient outcomes and reduces overall expenditure in medical treatments.
Agile Manufacturing
In the consumer goods sector, the ability to produce small batches allows companies to respond quickly to market trends and demands. This agility ensures you aren’t stuck with large inventories of unsold items, further driving down costs and increasing your responsiveness to consumer needs.

Industrial Applications Across Sectors
Aerospace and Defense
The aerospace and defense industries are among the earliest adopters of 3D printing technology. Given the high costs of materials and the critical need for precision, 3D printing offers invaluable benefits.
- Lightweight Components: The ability to create complex, lightweight structures without compromising strength helps reduce fuel consumption and improve efficiency.
- Replacement Parts: On-demand manufacturing of replacement parts significantly cuts down lead times, ensuring that aircraft and equipment are operational sooner and reducing downtime costs.
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector leverages 3D printing for rapid prototyping, custom parts, and even end-use components.
- Prototyping: The ability to quickly prototype new designs allows for more innovative solutions and rapid iteration.
- Efficiency Improvements: Custom jigs, fixtures, and gauges minimize errors and streamline processes on the manufacturing floor.
Healthcare
In healthcare, 3D printing is revolutionizing how medical devices, implants, and even pharmaceuticals are produced.
- Prosthetics and Orthotics: Custom-made prosthetics are more comfortable and functional while being more affordable.
- Surgical Instruments: The production of custom surgical guides and instruments tailored to individual patients enhances the precision of medical procedures.
Consumer Goods
Retail and consumer goods industries are also finding applications for 3D printing, from custom fashion to bespoke electronics.
- Tailored Products: Companies offer personalized products, driving customer satisfaction while keeping inventory costs low.
- Prototyping: Rapid prototyping allows for the quick testing of new product designs, reducing the time to market.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing 3D Printing
While 3D printing offers numerous advantages, there are also challenges to consider. These include high initial investment costs, limitations in material selection, and issues with production speed for certain applications. However, advancements in technology are continually addressing these challenges.
Initial Investment
While the upfront cost of 3D printers and materials can be high, the return on investment comes from the long-term savings in reduced labor, material costs, and improved efficiency. Careful planning and phased implementation can help manage these initial costs.
Material Limitations
Currently, not all materials are suitable for 3D printing, and some may not offer the same performance characteristics as traditionally manufactured materials. Continuous research and development are expanding the range of materials, enhancing the suitability of 3D printing for various industrial applications.
Production Speed
For high-volume production, 3D printing may not always be the most time-efficient solution. However, hybrid approaches that combine 3D printing with traditional manufacturing methods can balance the need for speed and customization. Emerging technologies such as multi-jet fusion and metal additive manufacturing are also making 3D printing more viable for larger-scale production.

Future Trends in 3D Printing
The future of 3D printing looks promising with ongoing innovations poised to make the technology even more accessible and efficient.
- Advanced Materials: Research is focused on developing new materials with better properties, including composites and bio-compatible materials.
- Speed Improvements: Advances in printing speeds and multi-material capabilities are anticipated to make 3D printing more competitive with traditional manufacturing.
- Integration with IoT and AI: The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) promises further automation and optimization of 3D printing processes, leading to additional cost reductions and increased efficiency.
Conclusion
3D printing is transforming industries by offering cost-effective solutions for prototyping, manufacturing, and customization. From reducing material waste and labor costs to enabling the production of complex and customized components, the benefits of adopting 3D printing are compelling. While there are challenges to address, the ongoing advancements in technology are poised to make 3D printing an even more integral part of industrial production processes in the future.
By embracing 3D printing technology, you can unlock significant cost savings and position your business at the forefront of innovation, paving the way for enhanced operational efficiency and competitive advantage in your industry.
About Ultimate 3D
Learn everything there is to know about 3D Printers and the different components and printing materials.
Site Links
Copyright 2024 Ultimate 3D








Be the first to leave a comment